Chickens can get sick for a variety of reasons. It is important to recognize these chicken diseases quickly and to respond appropriately. Untreated diseases can lead to the death of the chicken. In addition, some diseases are very contagious and the sick chickens must be separated as soon as possible.
Many diseases can be treated well with, for example, an antibiotic or other medicines, but some diseases cannot be treated and these must therefore be prevented as much as possible by good hygiene and housing.
Common Chicken Diseases

There are many types of chicken diseases, each with its own symptoms and treatment. Because some diseases can be very similar, it is good to know which diseases all exist. Below are a number of diseases that can occur in chickens.
1. Worms
Chickens can get a variety of worms, including roundworms, tapeworms, and hookworms. Worms reside in the chicken’s intestines where they live off the digested food. They can cause infections and emaciation that can even lead to the death of the chicken. Worms are in disinfected feces of, for example, birds that are eaten by insects. Chickens that eat these insects can contract worms as a result.
Reading suggestions; Rabbit Diseases – All You Need To Know
2. Red Mite

A red mite, or rather a red mite, feeds on the blood of a chicken. During the day they are in the cracks of the coop and at night they attack the chickens. They can also transmit diseases. Red mites can also cause tired chickens and in the worst case, a chicken will die from this.
3. Versluis
A feather louse or feather mite feeds on the proteins from the feathers of a chicken. They are less serious than red mites and mainly cause itching in the chickens. Chickens that scratch a lot or have cuts and bald spots can be infected with feather lice.
4. Coccidiosis
Coccidiosis is caused by an intestinal parasite that chickens can ingest through contaminated feces. The parasites can best multiply in a humid environment. They can infect the chickens through food and drinking water contaminated with feces, after which they can damage the intestinal wall of the chicken. A chicken can also eventually lose weight and die from coccidiosis.
5. Lime Feet
Scabies feet are caused by scabies mites in chickens. The parasite lives between the scales of the chicken leg and causes the chicken to itch. Eventually, the legs will swell because the parasite leaves its feces between the scales. This can cause subcutaneous inflammation and bleed on the legs. This may cause the chicken to have difficulty walking.

6. Snot
Chicken snot is caused by bacteria and is very contagious. Infected chickens appear cold. They cough, sniffle and have watery eyes. Chickens with poor resistance are especially susceptible to this disease.
7. Marek’s disease
Marek’s disease is caused by a serious virus that affects the nervous system and organs. Only chicks are susceptible to the contagious virus until the sixteenth week. Symptoms include difficulty walking, paralysis and death of the chick.
8. Laying Shortage
In case of laying need, a chicken literally cannot lose its egg. Laying deficiency can arise from calcium deficiency, an egg that is too large, a chicken that is too fat, a fallopian tube infection, development of an egg in an immature chicken or not being able to find a nest. Because the egg cannot leave the fallopian tube, inflammation can develop that can even cause a chicken to die.
9. Salmonella
Chickens can become infected with Salmonella by eating contaminated material, such as food, sand or vermin feces. The bacteria are present in the intestine and cause watery stools. Salmonella can in some cases enter the chicken’s bloodstream and thus contaminate the meat and eggs. Some Salmonella species can also make people sick from eating the contaminated eggs or contaminated meat.
10. Favus
Favus is a fungal infection that is often on the comb and wattles of the chicken. It can be recognized by white spots or flaky crusts. If left untreated, the infection can spread to other parts of the chicken. At this stage, the chicken usually gets sick and can eventually even die.
11. Aspergillosis
Aspergillosis is a fungal infection that affects the lungs of chickens. The fungus is found in contaminated soil and contaminated feed and can be inhaled by the chicken through airborne spores. This can cause the chicken to develop breathing problems. Especially in young chickens, the symptoms can be severe and in many cases, they will even die.
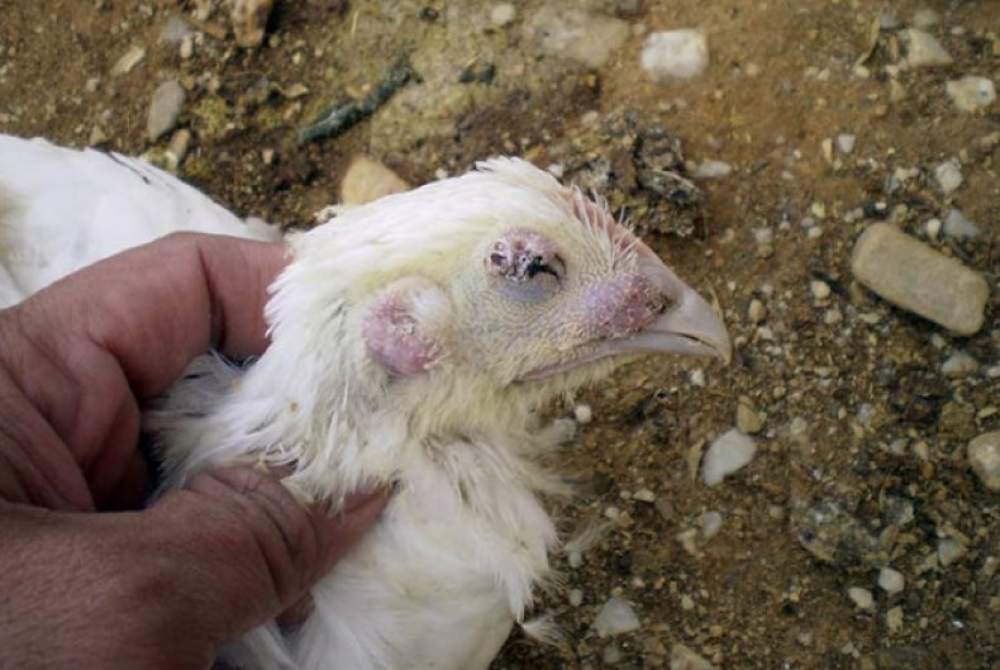
12. Follow-up flu
Bird flu is caused by the contagious virus influenza A. The virus can be transmitted by other birds and through contaminated materials or feces. Chickens with bird flu can have various symptoms such as respiratory problems, trachea infections, swollen head, disturbed egg production, fluid retention, listlessness, diarrhea, subcutaneous bleeding, tearing, and nasal cavity inflammation.
There is low pathogenic bird flu, highly pathogenic bird flu, and pseudo bird flu. All three variants are contagious to humans, but the highly pathogenic bird flu is the most dangerous. People can even die from this if infected.
What are the Chicken Diseases Symptoms?
A sick chicken will often show deviant behavior. For example, a chicken can remain aloof, be drowsy or scrape little. This behavior often indicates a disease. It is also important to keep an eye on the feces of the chickens. If it is watery or bloody, it indicates a sick chicken. Feces can also contain worms. Bald spots or itching outside of the molting period can also indicate a disease.
Often these symptoms are related to red mites or feather mites. Also, pay attention to the appearance of the chickens. Slimming or swollen legs are usually a sign of a sick chicken. After all, egg production says a lot about the welfare of a chicken. A sick chicken will often have reduced egg production. But shorter days, a molting period, broodiness, incomplete nutrition, or old age can also be a cause for a reduced laying.
Reading suggestions; Chicken Names – 400+ Good and Funny Chicken Names
Therapy
Many chicken diseases can be treated. In many cases, it is good to contact a veterinarian who specializes in poultry if you have any of the above symptoms. In some cases, you can also take steps yourself to remedy the disease.
For example, anti-worm treatments are readily available and feather lice can be well prevented by treating chickens preventively. The most important thing is to keep a close eye on the chickens and spot symptoms. Untreated chicken diseases can have serious consequences. Especially in the summer, the chickens have to be monitored extra. Many diseases mainly occur when it is warm. There are also ways that the chickens are less likely to get sick.
How do you prevent sick chickens?
By keeping the food clean you can prevent many infections as much as possible. Buy good feeding troughs, preferably one that the chicken can open itself. Also, ensure a clean and dry loft. Many diseases can develop better in a moist environment. Ventilation and a good ground cover that stays dry are therefore very important. Also regularly disinfect the loft and materials.
This kills bacteria and fungi that can make chickens sick. After all, many diseases are transmitted through contaminated feces. Therefore, make sure that no other birds can defecate in the run and that vermin stays away from the coop. Also regularly clean up the feces of the chickens.









